Ventilation plays a crucial role in sustainable building design, contributing to energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and overall environmental impact. Here are key considerations for ventilation in sustainable building design:
Natural Ventilation:
- Concept: Leverage natural airflow to reduce reliance on mechanical systems. This involves designing the building to capture and utilize prevailing winds, temperature differentials, and outdoor air quality.
- Benefits:
Energy Efficiency: Reduces the need for mechanical ventilation systems, lowering energy consumption.
Indoor Air Quality: Enhances air quality by bringing in fresh outdoor air.
Cost Savings: Can lower initial construction and operational costs.
2. Energy-Efficient Mechanical Ventilation:

- Concept: When mechanical ventilation is necessary, opt for energy-efficient systems. This includes using variable speed fans, energy recovery ventilators (ERVs), and demand-controlled ventilation (DCV) systems.
- Benefits:
Energy Savings: Reduces energy consumption and operating costs.
Climate Control: Improves control over indoor temperature and humidity.
Green Building Certification: Aligns with sustainability standards, contributing to certifications like LEED or BREEAM.
3. Heat Recovery Ventilation (HRV) and Energy Recovery Ventilation (ERV):

- Concept: HRV and ERV systems recover and reuse heat or energy from exhaust air to precondition incoming fresh air, minimizing energy loss during ventilation.
- Benefits:
Energy Efficiency: Maximizes energy recovery, reducing the need for additional heating or cooling.
Improved Indoor Comfort: Helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature.
Carbon Footprint Reduction: Lowers the overall environmental impact of the building.
4. Occupancy Sensors and Demand-Controlled Ventilation:
- Concept: Implement sensors to detect occupancy levels and adjust ventilation rates accordingly. This ensures that ventilation systems operate based on actual needs rather than a fixed schedule.
- Benefits:
Energy Savings: Reduces unnecessary ventilation when spaces are unoccupied.
Improved Indoor Air Quality: Ensures adequate ventilation during occupied periods.
Compliance with Building Codes: Adheres to regulations requiring ventilation based on occupancy.
5. Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS):
- Concept: Integrate ventilation systems with a centralized BMS to enable real-time monitoring and control of indoor environmental conditions.
- Benefits:
Optimal Performance: Allows for dynamic adjustments in response to changing conditions.
Predictive Maintenance: Facilitates proactive maintenance, minimizing downtime and energy waste.
Data Analytics: Enables data-driven insights for continuous improvement in energy efficiency.
6. Green Roof and Living Wall Systems:
- Concept: Incorporate green roofs and living walls to improve insulation, reduce the urban heat island effect, and enhance natural ventilation through the use of vegetation.
- Benefits:
Thermal Regulation: Mitigates temperature extremes and reduces the need for heating and cooling.
Biodiversity: Supports biodiversity and ecological balance.
Aesthetic and Psychological Benefits: Enhances the overall aesthetics and occupant well-being.
7. Commissioning and Regular Maintenance:
- Concept: Regularly commission and maintain ventilation systems to ensure they operate at peak efficiency. This involves periodic inspections, adjustments, and cleaning.
- Benefits:
Sustainable Performance: Ensures that ventilation systems continue to meet design intent.
Energy Efficiency: Prevents energy waste caused by inefficient or malfunctioning systems.
Long-Term Cost Savings: Reduces the likelihood of major repairs or premature system replacement.
By integrating these ventilation strategies, sustainable building design can optimize energy use, enhance indoor environmental quality, and contribute to a reduced environmental footprint over the life cycle of the building.
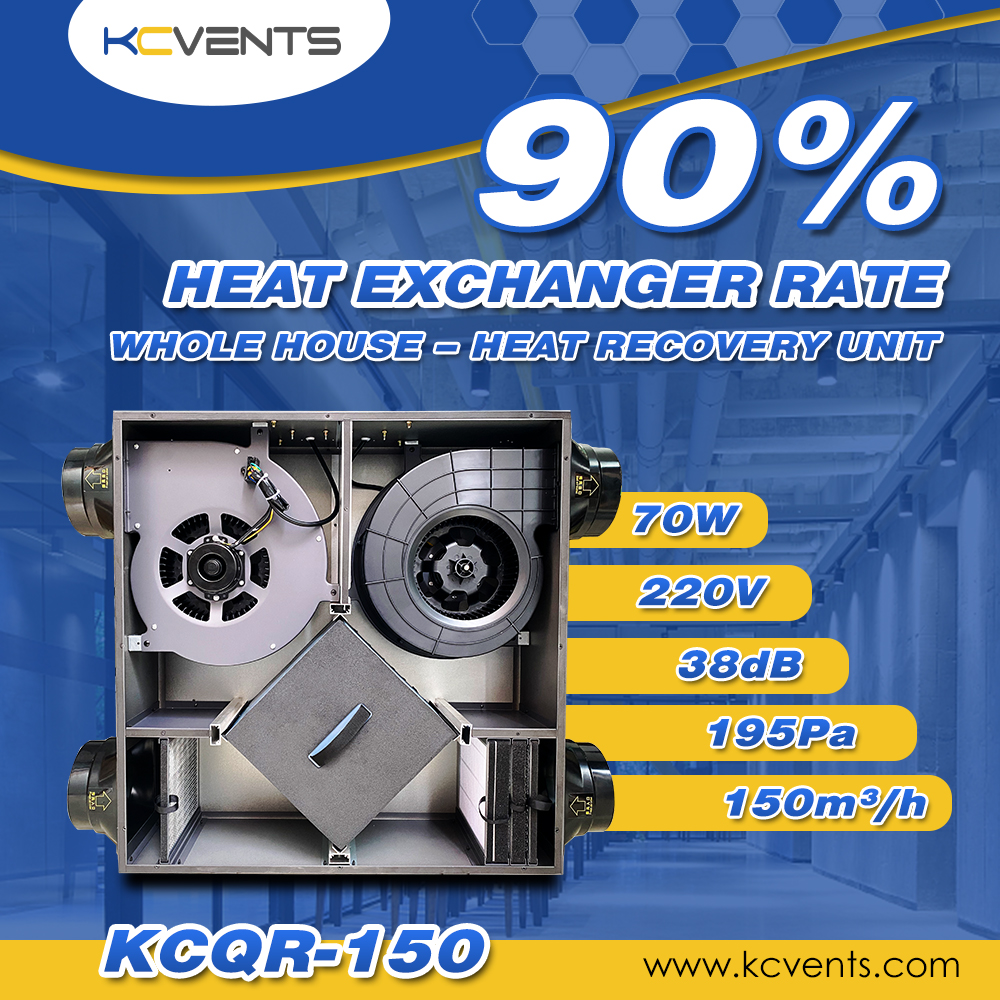
KCVENTS Air heat recovery units work in a ventilation system to recover and transfer heat streams, typically exhaust air and incoming fresh air. The primary goal of these units is to improve energy efficiency and reduce heating or cooling costs in buildings.


